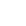
Eye swab
Eye swab is used for diagnostics, monitoring, and determining the treatment in patients with various eye infections such as blepharitis, conjunctivitis, and keratitis.
Eye infections are common, especially in children, and can be caused by various microorganisms: bacteria, viruses, and fungi. These pathogenic microorganisms can enter the eye through hands, contact lenses, foreign bodies, after surgery, etc.
What does an eye infection involve?
- Mild eye infections include conjunctivitis (“red eye”) and blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids).
- Conjunctivitis can occur in combination with an infection of the eyelid or cornea.
- Less common but more serious infections include keratitis (inflammation of the cornea) and intraocular infection (within the eye).
- Other eye infections include dacryoadenitis (inflammation of the tear gland), dacryocystitis (inflammation of the tear sac), inflammation of the tear ducts, and cellulitis
Who are the most common causes of eye infections?
In addition to viruses, bacteria are the most common causes of eye infection, which is why it is advised to do an eye swab if persistent symptoms do not improve.
Among bacterial pathogens, the most common ones are:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Species of Corynebacterium
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Haemophilus influenzae
- Less common causes include Streptococcus groups A, C, and G, Neisseria cinerea, Propionibacterium acnes, species of the Moraxella genus and other gram-negative microorganisms, as well as anaerobic microorganisms such as Eubacterium and Peptostreptococcus genera.
How is an eye swab performed?
First, the skin around the eyes is cleaned with a mild antiseptic. The patient should sit with the head tilted back. Then, the doctor pulls down the lower eyelid and gently swabs, in a rotating motion, from the conjunctiva over the inner side of the lower eyelid to the outer corner of the eye.
What happens after receiving the results?
After receiving the results of the eye swab, the doctor can make a diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment.