Hiperbaric Chamber
A hyperbaric chamber, also known as recompression therapy, is a non-invasive medical treatment aimed at increasing the oxygen levels within your body. In the medical field, it’s referred to as Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) and is commonly used in conditions such as carbon monoxide poisoning, decompression sickness, and slow-healing wounds.
What does the therapy involve?
HBOT involves sitting or lying in a hyperbaric chamber – a closed space filled with oxygen at high pressure – and breathing this air. This allows your lungs to take in more oxygen, thereby increasing the circulation of oxygen in your bloodstream.
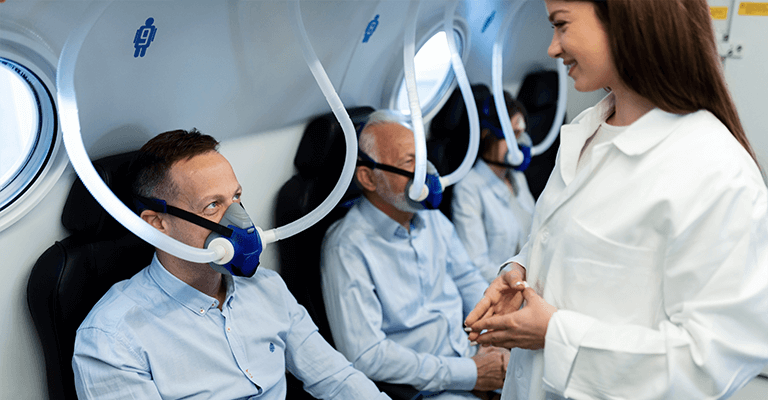
Some hyperbaric chambers are designed for treating only one person (single-seat chamber), while there can also be chambers intended for multiple individuals simultaneously (multi-seat chamber). In a multi-seat chamber, you’ll receive oxygen treatment through a specialized mask.
Once the chamber doors are sealed, you might hear a slight hissing sound (indicating the chamber filling with oxygen) and the pressure inside gradually increases. The hyperbaric chamber experience is generally comfortable and relaxing for you, though the increased air pressure might feel similar to being in an airplane at higher altitudes or atop a mountain. Any resulting pressure in your ears can be relieved by yawning. During the therapy, you should breathe normally.
How does Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy work?
A hyperbaric chamber is a closed space under high pressure filled with pure oxygen.
The air pressure inside the hyperbaric chamber is two to three times higher than in a typical room, enhancing the absorption of oxygen. Therefore, while regular room air contains 21% oxygen, a hyperbaric chamber provides air containing 100% oxygen.
The therapy works by delivering controlled oxygen flow, an essential element for human life. Oxygen is absorbed into your lungs, entering the bloodstream, traveling to the heart, and then circulating to all tissues in your body.
HBOT delivers pure oxygen under high air pressure, helping the body take in more oxygen necessary for successful treatment of specific conditions.
For instance, higher oxygen levels in the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord might aid in neuron regeneration after a stroke. Increased oxygen concentration in lymph fluid can help clear toxins from lymph nodes and strengthen your immune system.
What is it used for?
The hyperbaric chamber contains healthy oxygen, aiding your immune system in fighting bacteria and generating stem cells. Stem cells are special cells in your body that help create other vital types of cells, including blood cells, brain cells, and muscle cells.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy assists your body in healing. For tissues in your body to function properly, they require sufficient oxygen. If your tissues are injured, they need even more oxygen. The increased pressure in the hyperbaric chamber helps your blood carry oxygen throughout your body and also aids your white blood cells in protecting your body from infection.
What are the benefits of the hyperbaric chamber?
HBOT helps increase oxygen levels in the blood, believed to assist the body in the following ways:
- Boosts the immune system
- Reduces inflammation in the body
- Improves circulation
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy can be used as a standalone treatment or as a procedure that may enhance the effectiveness of medications such as antibiotics.
The most significant advantages of this type of therapy include:
- Accelerated recovery after injury or surgery
- Stimulates stem cell production and rejuvenates existing cells
- Promotes collagen production
- Reduces pain and bruising
- Alleviates swelling and inflammation
- Excellent for calming the mind and improving brain function
- Increases energy levels
What are the indications?
Considering the mode of action and the listed beneficial effects of HBO therapy, there are scarcely any areas of medicine where hyperbaric oxygenation isn’t applied today.
Emergency Medicine:
• Gas gangrene,
• Arterial gas embolism,
• Carbon monoxide and cyanide poisoning,
• Decompression sickness,
• Acute traumatic ischemia (crush injuries and compartment syndrome),
• Sepsis.
Surgery:
• Soft tissue infections,
• Necrotizing fasciitis,
• Chronic wounds,
• Arterial, venous, and mixed ulcers,
• Diabetic foot,
• Diabetic phlegmon,
• Gangrene,
• Decubitus ulcers.
Vascular Surgery:
• Atherosclerosis,
• Acute and chronic arterial insufficiency,
• Ischemic changes in the lower extremities,
• Buerger’s disease,
• Raynaud’s disease,
• Vasculitis.
Neurology:
• Multiple sclerosis,
• Migraines,
• Cluster headaches,
• Polyneuropathies of various etiologies (diabetic, alcoholic, drug-induced),
• Post-stroke conditions,
• Trigeminal neuralgia,
• Parkinson’s disease,
• Dementia.
Dermatology and Venereology:
• Pyoderma gangrenosum,
• Psoriasis.
Rheumatology:
• Systemic sclerosis,
• Osteoporosis,
• Rheumatoid arthritis,
• Lupus,
• Fibromyalgia.
Orthopedics and Traumatology:
• Dysbaric osteonecrosis,
• Aseptic necrosis of the femoral and humeral heads,
• Chronic refractory osteomyelitis.
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery:
• Compromised skin grafts,
• Burns,
• Frostbite.
Urology:
• Fournier’s gangrene,
• Postradiation cystitis,
• Vascular impotence.
Gynecology:
• Infertility
ENT (Ear, Nose, Throat):
• Acute deafness,
• Malignant external otitis,
• Tinnitus,
• Bell’s palsy.
Ophthalmology:
• Central retinal artery occlusion.
Hematology:
• Severe anemia.
Gastroenterology:
• Ulcerative colitis,
• Crohn’s disease.
Sports Medicine:
• Treating sports injuries of muscles, bones, tendons,
• Accelerating recovery after exhaustive competitions and training.
Oncology:
• Postradiation necrosis of skin and soft tissues,
• Increasing radiosensitivity of tumor tissue.
Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation:
• In rehabilitation after stroke, coronary disease, peripheral vascular diseases, paralysis, and paraplegia, toxic encephalopathy.
Neurosurgery:
• Cerebral abscess,
• Traumatic brain injuries.
Dentistry:
• Osteomyelitis of the mandible,
• Infections after dental surgeries and tooth extractions,
• Pre and post-implant placement.
Anti-aging
Post-COVID Syndrome
How long does Hyperbaric Therapy last?
Each hyperbaric therapy session lasts about an hour. The number of treatments you’ll need will largely depend on your health condition.